
This all means that 1 watt is equal to 1 kg.m 2 / s 3.
Thus, 1 Newton is equal to 1 kg.m / s 2, and 1 Joule is equal to 1 kg.m 2 / s 2 because it’s essentially defined as 1 Newton per meter. A Newton is a unit of force defined as the force which gives 1 kilogram of mass an acceleration of 1 meter per second squared. The reason for this is that 1 Joule can be defined as the energy transferred when a force of 1 Newton displaces a mass through a 1-meter distance.

© Other Ways to Define Wattsġ Watt is also equivalent to 1 kg.m 2 / s 3, or 1 kilogram meter squared per second cubed. To light up properly, this 60-watt bulb requires 60 joules of energy to be transferred each second the light is on. A 40-watt light bulb, for example, requires 40 Joules of energy to be transferred per second to run optimally. In this way, 1 watt is equivalent to 1 Joule of energy being transferred per second. In practical terms, watts can be thought of as the power it takes to do something or the energy used by a device, such as turning on a light bulb. Watts are used as the standard unit of power for quantifying the rate of this energy transfer. Therefore, power is the rate of energy transfer or the amount of energy converted per unit of time. In this case, work refers to the energy transferred from one object to another. In comparison, watts can be thought of as a unit of power, or the rate at which “work” is done. Amperage means the current that can flow through, and is measured in amps. Therefore, an amp is the rate at which current is flowing. Put simply, a coulomb quantifies an amount of electric charge and an amp measures how fast the charge is moving past the point in space. 1 coulomb is defined as the amount of electric charge carried in 1 second by a 1 amp current. As such, 1 amp is equivalent to 1 coulomb’s worth of charge moving past a given point in 1 second. This is a French organization responsible for establishing standardized scientific measurements. The Definition of AmpsĪmperes, or amps for short, are always defined within the International System of Units (SI), which was created by the Bureau International des Poids et Mesures (BIPM).

This is how amps and watts are denoted when used in calculations and equations, as well as how they’re measured and listed on electrical devices. To signify either, it’s simple - the first letter from both is taken to give A and W respectively. SymbolsĪs far as the mathematical symbols used, things are kept fairly simple for amps and watts. Now we’ve defined amps and watts and their units, it’s time to look closer at the differences between them. Unit of power, or the rate at which work is doneĬ / s: 1 coulomb, or 6.24 x 10 18 electrons worth of charge moving past a given point in 1 second. Without further ado, let’s get into a comparison and explanation of amps vs.

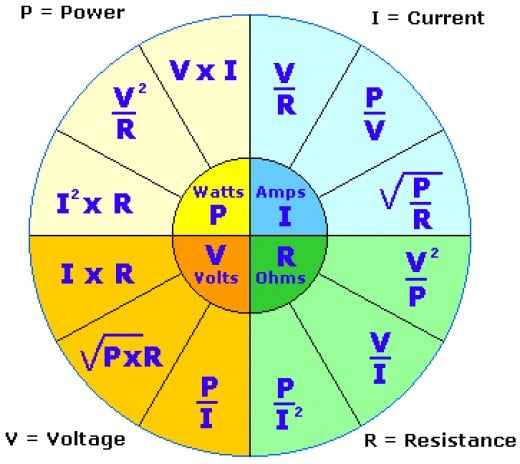
Understanding exactly what things like amps and watts mean is crucial to safely take on any sort of electrical project, and can be hugely beneficial if you’re looking to save money on your energy bills. However, when it comes to how electricity works and the terms and measurements used to describe it, things can get a little more complicated and less intuitive. As well as this, the potential dangers of electricity are well-established. The way it can be used to power our lights, AC, homes, favorite devices and even our new electric vehicles. Always check the electrical requirements for the item that you are installing to determine whether or not the item will require its own dedicated circuit.Generally, people are aware of electricity, or at least its effects. For example, if you attempt use a microwave, a space heater, and a vacuum cleaner at one time and all three electrical outlets being used are connected to the same circuit, you will trip the breaker requiring you to perform a reset. Understanding how the three terms relate helps with understanding the electrical requirements of an item.Īmps X Volts = Watts (Amount X Force = Workload)Įlectrical items require a certain number of watts to run, and if the total watts exceed what the circuit can handle, the circuit kills the power as a safety precaution. Amps multiplied by volts gives you the total wattage (workload). Volts are the measure of the force of the electric. Amps are simply the amount of electricity used by the item. Often you will see amps, volts and watts listed on electrical items. Electricity is described by three terms: Amps (amperage), Volts (voltage), and Watts (wattage).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
